The foreign exchange market is the market where one country's currency is traded for another's. The foreign exchange market is the world's largest financial market. Most of the trading in the foreign exchange market takes place in US Dollars, Euros, British Pounds, Japanese Yen and Swiss Francs. Participants in foreign exchange markets typically include:
1. Companies that import goods may need to convert their domestic currency to the foreign currency to pay for goods from the foreign country.
2. Companies that export goods may receive foreign currency for these goods, and need to convert this currency to the domestic currency.
3. Investors who buy and sell foreign stocks and bonds.
4. Foreign exchange brokers who maych buy and sell orders.
5. Traders in the foreign exchange market.
Exchange rate: The price of one country's currency expressed in terms of anohter country's currency. In practice, most exchange rates are in terms of US dollars.
Triangular arbitrage: Most exchange rates are in terms of US dollars because it reduces the likelyhood of triangular arbitrage. For example, between the US Dollar, Euro, British Pound, Swiss Franc, Japanese Yen, Canadian Dollar, Australian/New Zealand Dollar, and South African Rand, there would be 28 potential exchange rates. To reduce the likelihood of inconsistencies, we write exchange rates in terms of US dollars, and use this exchange rate to determine the implied cross rates between two foreign currencies.
Spot exchange rate: The spot rate is the price that is quoted for immediate settlement, typically within one or two days.
Forward rate: The forward exchange rate is the price that is agreed to exchange one currency for another sometime in the future - the rate of a forward contract on a currency. The forward rate is typically a function of the spot rate and the difference in interest rates between two countries i.e. the forward rate includes a premium or discount reflecting the interest rate differential between the two countries.
Swap rate: A swap occurs when one party agrees to sell a currency and repurchase it sometime in the future. The swap rate is the difference between the sale price and the repurchase price.
Purchasing power parity: The law of one price (LOP) determines the spot exchange rate. This law, using purchasing power parity, says that the cost of a commodity should be the same across countries. Assume SUSD(t) is the spot rate between the US dollar and the CAN dollar (that is, the number of Canadian dollars needed to purchase a US dollar), PCAD(t) is the price of a commodity, say wheat, in Canada and PUSD(t) is the price of wheat in US dollars. If the price of wheat is 316.55 in Canadian dollars, and 304.32 in US dollars, we can estimate the spot exchange rate.
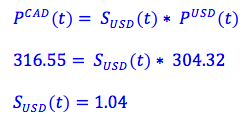
Interest rate parity: The forward rate and the spot rate are related by the same sort of arbitrage that underlies the law of one price. If the forward rate is greater than the spot rate, the forward rate is considered to be at a premium. If the forward rate is less than the spot rate, it is said to be at a discount. That is, if one country has a higher interest rate then the other, we know that we would have to borrow more today in that currency to buy one commodity in the future.
Exchange rate risk: According to Geczy, Minton and Schrand, 41 percent of Fortune 500 companies attempt to hedge their foreign currency risk. Currency swaps, currency options and other financially engineered products are used by businesses to hedge foreign exchange rate risk.
Photo by Christine Roy on Unsplash
© BrainMass Inc. brainmass.com June 30, 2024, 8:33 am ad1c9bdddf