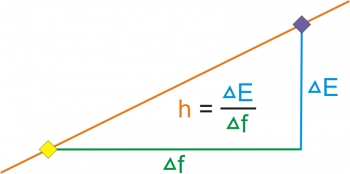Quantum physics is a branch of physics which deals with physical phenomena’s at microscopic scales, where the action is on the other of Planck constant. Quantum mechanics departs from classical mechanics primarily at the quantum realm of atomic and subatomic length scales. Quantum mechanics provides a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter.
The mathematical formulations of quantum mechanics are abstract. A mathematical function known as the wavefunction provides information about the probability amplitude of position, momentum, and other physical properties of a particle. The wavefunction treats the objet as a quantum harmonic oscillator, and the mathematics is akin to that describing acoustic resonance. Many properties in quantum physics cannot be easily visualized in terms of classical mechanics.
According to Planck, each energy element E is proportional to its frequency v:
E=hv
Where h is Planck’s constant. Planck insisted that this was simply an aspect of the processes of absorption and emission of radiation and had nothing to o with the physical reality of the radiation itself.
Quantum mechanics had great success in explaining many of the features of our World. It is often the only tool available that can reveal the individual behaviors of the subatomic particles that make up all forms of matter. Quantum physics has also strongly influenced string theories, candidates for a theory of everything.
© BrainMass Inc. brainmass.com June 30, 2024, 9:26 am ad1c9bdddf