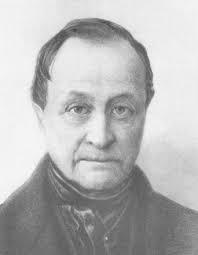The field of sociology is the study of human social behaviour, especially the study of the origins, organization, institutions, and development of human society. Sociologists typically use a macro-level lens to learn more about society and the structures it is comprised of.
The actual term 'sociology' was coined by Auguste Comte, the father of sociology in 1838. Comte felt that science and scientific analyses and methodology could be used to study the social world and discover the laws that govern our social lives. He introduced positivism to sociology, which implies that the social world can be understood based on scientific facts.
The three theorists from the 19th and 20th century that are most often cited in sociology are Karl Marx, Emile Durkheim and Max Weber. All three men were originally trained in other academic disciplines but have contributed immensely to the modern academic field of sociology.
The field of sociology has three major theoretical frameworks through which to view society:
- Structural Functionalism
- Conflict Theory
- Symbolic Interactionism
To learn more about these frameworks and the popular theorists that contribute to them, please further explore this section of BrainMass.
The traditionally popular fields of study within sociology include stratification, social class, culture, race and ethnicity, gender and sexuality, social mobility, secularization, law and deviance. In recent decades, sociologists have learned that basically all spheres of human activity are affected by the social structures within they operate, fields such an environment, health and military have opened up in the sociological discipline.
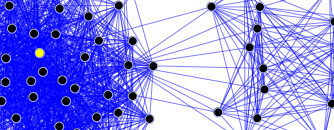
Sociological methodology has also been expanding significantly in the last few decades. Social researchers now use a variety of qualitative and quantitative techniques. While the field classically had an interpretive and philosophical approach to the analysis of society, recent decades has given to the rise of mathematically analytical and positivist techniques, such as social network analysis.
© BrainMass Inc. brainmass.com June 29, 2024, 12:31 am ad1c9bdddf