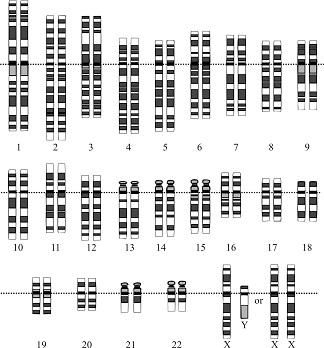
Genes are discrete units of inheritance that compose helices of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) located in the nucleus of cells. On a microscopic scale, genes contain genetic information that codes for specific amino acids; this produces chains of polypeptides that maintain the internal conditions of the organism. On a macroscopic scale, the genes make up the genotype of an organism, this gives rise to the observed properties of the organism called the phenotype – examples are appearance, hair color and behavior.
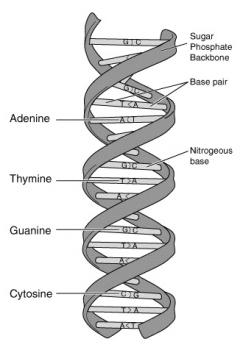
Genes contain specific permutations of nucleotides. Nucleotides are the monomers of DNA, and are composed of three components: nitrogenous base, five-carbon sugar and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous bases are adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine. Complementary base pairing ensures that within the DNA helix, adenine pairs with thymine with two hydrogen bonds whilst cytosine and guanine pair with three hydrogen bonds. Three nucleotides form a codon, and this corresponds to the production of specific amino acids – thus, gene sequence is integral in protein synthesis.
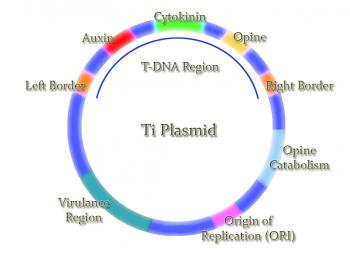
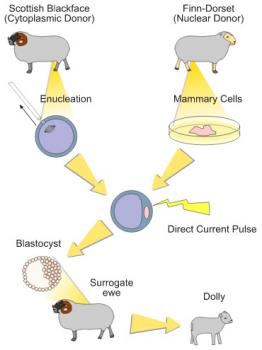
Advances in technology has led to the ability to manipulate DNA as seen in recombinant DNA and cloning. Recombinant DNA uses sequences of DNA from two or three different species which are inserted into a plasmid by usage enzymes; it is then inserted into a host organism where replication and expression occurs. An example of recombinant DNA is in the production of insulin and GMO crops. Cloning is the replication of genetic codes, where a cell taken from parent and inserted into an ovum, where then it is embedded into the uterus and carried through a normal pregnancy. The offspring will be a genetic clone of the parent - notable example is Dolly the sheep.
© BrainMass Inc. brainmass.com June 30, 2024, 9:26 am ad1c9bdddf