The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is the cost of financing for new projects found by looking at the firm's financing options, both debt and equity, as a fixed basket. When a firm undertakes a new project, it typically finances the project with one source of financing: either cash, debt or equity. However, we know that in practice most firms have a target capital structure. That is, using debt this time will reduce the firm's debt capacity, and they will likely raise equity next time. If we use cash this time, it has a related opportunity cost.
We therefore use the firm's target capital structure as representing the fixed mix of debt and equity of the firm over the long-term (even if it varies in the short-term). We typically exclude short-term liabilities when comparing our debt to equity when the firm's short-term liabilities do not reflect the firm's permanent financing (for example, accounts receivable and a short-term line of credit would be excluded because they reflect sales or seasonal needs, not permanent financing needs). However, if a short-term bank loan was used as part of the firm's permanent capital structure, it would be included.
The unadjusted weighted average cost of capital is equal to the cost of equity times the proportion of the firm's capital strucutre composed of equity, plus the firm's cost of debt times the proportion of the firm that is financed with debt.
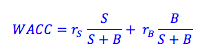
Where,
rS = the rate of return on equity
rB = the rate of retun on debt
S/(S+B) = the proportion of the firm financed with debt
B/(S+B) = the proportion of the firm financed with equity
The adjusted weighted average cost of capital takes into account the fact the interest rate payments on debt are typically tax deductible, and thus the after-tax cost of debt is what we need to compare with the cost of equity (which is inherently after tax), and after-tax cash flows when using WACC to value a project.
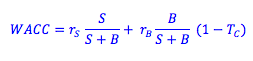
The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) can be used in a net present value (NPV) analysis as the rate of return required for a project undertaken by a levered firm.
Photo by freestocks.org on Unsplash
© BrainMass Inc. brainmass.com June 28, 2024, 7:04 pm ad1c9bdddf