Income taxes are an accrued expense that is based on the amount of the company's net income. As income tax expense accrues, a corresponding liability is credited, meaning that the expense will eventually become payable. There is some dispute about whether income taxes payable are an estimated liability because uncertainty exists where the amount owed is subject to restatement by the Internal Revenue Service.
If a small corporation has a profit of $100,000 at the end of the year and is taxed at 35%, its tax liability at the end of the year would be $35,000 (assuming it made no installment payments during the year).
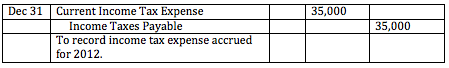
Most corporations are required to make income tax payments in installments throughout the year, usually estimated based on the income tax payable for the previous year. Last year the company had to pay $35,000 in income tax. Using this number to estimate this years quarterly installments, the company would have to pay $8,750 each quarter. Each installment payment reduces the company's income taxes payable account.

An alternative approach is to charge each installment payment to income tax expense, and then adjust the expense account at the end of the year when the actual income tax expense becomes known. Both approaches will lead to the same amount of expense, liability and payment amounts being recognized in the year.
In the future, if the Internal Revenue Agency reassesses an additional tax on an earlier years' income, the expense is charged to the current period's operations. At the same time, either the income taxes payable account will be increased or the cash account will be credited (if the expense is paid right away).
- Business
- /
- Accounting
- /
- Financial Accounting & Bookkeeping
- /
- Accounting for Liabilities
- /
- Current Liabilities
- /
Income Taxes Payable
BrainMass Solutions Available for Instant Download
Differences between the following components of taxable income
What are the differences between the following components of taxable income? Provide at least one example of each. o Deductions for AGI and deductions from AGI o Gross income and AGI o AGI and taxable income o Tax deduction and tax credit o Personal exemption and dependency exemption
Matteo working overtime or repairing his car
30. Matteo, who is single and has no dependents, was planning on spending the weekend repairing his car. On Friday, Matteo's employer called and offered him $500 in overtime pay if he would agree to work over the weekend. Matteo could get his car repaired over the weekend at Autofix for $400. If Matteo works over the weekend, he
Taxes, Deductions, Exemptions, Tax Rates and Which Job to Take?
Rick, who is single, has been offered a position as a city landscape consultant. The position pays $125,000 in cash wages. Assume Rick files single and is entitled to one personal exemption. Rick deducts the standard deduction instead of itemized deductions. a) What is the amount of Rick's after-tax compensation (ignore payr
