The current ratio is found by dividing the firm’s current assets by the firm’s current liabilities. Current liabilities include the current portion of long-term liabilities, for example, interest payments on long-term debt that will become due within the year.
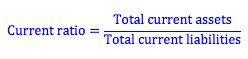
The current ratio gives us an idea about a firm’s ability to cover its short-term liabilities. That is, over the year we can imagine that the firm will be selling its inventory and collecting accounts receivable and, with the cash it already has in the bank or invested in marketable securities, it will be able to use these proceeds to pay interest on its debt and pay its accounts payable when they become due.
When a firm’s current ratio goes down, we may look at this trend as potentially signaling that the firm is entering financial distress. As a result, the firm may not be able to cover its short-term liabilities as easily as before.
Current Ratio
BrainMass Solutions Available for Instant Download
Industry Averages for Commonly Used Ratios
Obtain industry averages for commonly used ratios in the 2013 and 2014 period. Write a 350 word report comparing Disney ratios to the industry averages. Discuss whether Disney entertainment company is profitability, efficiency, liquidity, and solvency are better than, or worse than, two of its peers. Place the industry averages,
Short Term Solvency Ratios
HANDOUT: Useful Financial Ratios (see attachment) SHORT-TERM SOLVENCY RATIOS (Liquidity Ratios) Current ratio = Current assets ÷ Current liabilities Quick ratio = (Current assets - Inventory) ÷ Current liabilities ACTIVITY RATIOS Total asset turnover = Total operating revenues ÷ Average total assets Receivables turnov
The current ratio, change, and indicators of liquidity
What does a change in a current ratio mean to you? What is a good current ratio and does a high current ratio always indicate good liquidity?
Sherman's Current and Quick Ratio
The Sherman Company has been in the process of making small tanks and light armored vehicles for the past twenty years. Their clients cannot expend the kinds of funds necessary to acquire main battle tanks or other large scale weaponry, so their niche is very secure. Rommel/Patton Industries, a large tank builder, would like to
Inventory Turnover Ratio
3. Chaka Company had no prepaid expenses and inventories remained unchanged during the year. Other selected year-end data for the company includes the following: Cost of goods sold $1,500,000 Current liabilities 1,800,000 Current ratio 3.0 to 1 Acid-test ratio 2.5 to 1 What was the company's inventory turnover ratio f
Cash Flow Statements: Operating Cash Flow and Current Debt Ratio
Below is Steve Frim Company's statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31,2005: Steve Frim Company Statement of Cash Flows For the Year Ended December 31, 2005 (in thousands) Cash Flows from Operating Activities: $389 Net income Adjustmen
When auditing a medium-sized manufacturing corporation with two or three divisions, and using ratios to assess going concern, which of many different ratios would be the most useful ones to use? How do you determine which ratios are the ones that should be used? Calculate at least 5 ratios to assess going concern. My question is how The following ratios are available: current ratio acid test ratio gross profit ratio operating margin ratio net income ratio return on total assets ratio return on equity ratio Or another approach is which of the following four categories of ratios is appropriate? Liquidity Profitability Leverage Activity
See attached file. When auditing a medium-sized manufacturing corporation with two or three divisions, and using ratios to assess going concern, which of many different ratios would be the most useful ones to use? How do you determine which ratios are the ones that should be used? Calculate at least 5 ratios to assess goin
Explain and compute ratios: Current ratio, inventory turnover, acid test ratio, current ratio before and after dividend
Answer each of the questions in the following unrelated situations. (a) The current ratio of a company is 6:1 and its acid-test ratio is 1:1. If the inventories and prepaid items amount to $496,400, what is the amount of current liabilities? (Round answers to 0 decimal places eg 75,481) $ (b) A company had an average
Increased Current Ratio and Drop in Total Assets Turnover Ratio
You are a financial analyst for a pharmaceutical company and the CFO has asked you to look into the following situation. Over the past year, the company has realized an increase in its current ratio and a drop in its total assets turnover ratio. Sales have remained constant as have the quick ratio and the fixed assets turnover r
Current ratio of Kinetics, Inc.
Kinetics, Inc has total assets that equal $214,600 along with long term debt that equals $52,700, total equity equaling $119,500, fixed assets that equal $164,400 and finally sales that equal $241,900. If Kinetics Inc has a profit margin that is 6%, what is the current ratio?
Quick Ratio, Fixed Assets, Current Ratio Changes at SVF
Scenario: Jeff, Bob and I stopped by the old 'watering hole' for an attitude adjustment. Guess what? The conversation turned to work. Here is how the conversation unfolded. Over the past year, good old SVF (that's the name of the company) has realized an increase in our current ratio and a drop in total assets turnover ratio. Co
Strengthen current ratio
A firm wants to strengthen its financial position. Which of the following actions would increase its current ratio? I'm choosing e because of the fact that they can pay off the long-term debt and put themselves in a position of holding onto short-term debt. Is this correct? a) Use cash to increase inventory holdings.
Liquidity ratio current ratio and the acid test ratio
Calculate the liquidity ratio (current ratio and the acid test ratio) of the three organizations and analyze your results regarding ABC, kindred and northern Illinois medical center. As ABC only has one year of data, only use one year of data for the other two companies as well. Show calculations.
Deceptive Ratio Positions
Favorable business operations may bring about certain seemly unfavorable ratios. Unfavorable business operations may result in apparently favorable ratios. For example, a company increased its sales and net income substantially for the current year, yet the current ratio at the end of the year is lower than the beginning of the
Blockbuster ratios: quick, current liquidity, DuPont ratio, profit margin, asset utilization
Compute the quick and current liquidity ratios, the DuPont ratio, profit margin, asset utilization, and financial leverage. I would like to use Blockbuster.
Current Ratio and Quick Ratio
A firm's long term assets = $75,000, total assets = $200,000, inventory = $25,000 and current liabilities = $50,000 A. Current ratio = 0.5; quick ratio 1.5 B. Current ratio = 1.0; quick ratio 2.0 C. Current ratio = 1.5; quick ratio = 2.0 D. Current ratio = 2.5; quick ratio = 2.0
BMC Corp: Calculate ratios for ROE, quick, interest coverage, current, net profit margin
6. BMC CORPORATION INCOME STATEMENT FISCAL YEAR ENDING 12/31/2004 (DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS) Net Sales $1025 Cost of Goods Sold 682 Gross Profit Margin 343 Depreciation 31 Operating Expense 103 Administrative Expense 127 Operating Profit 82 Interest 27 Pr
BMC's Ratios: Calculate ROE, quick ratio, interest coverage, current ratio, profit margin
USE THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION FOR THE NEXT FIVE PROBLEMS BMC CORPORATION INCOME STATEMENT FISCAL YEAR ENDING 12/31/2004 (DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS) Net Sales $1025 Cost of Goods Sold 682 Gross Profit Margin 343 Depreciation 31 Operating Expense 103 Admini
Financial information for the current ratio measure
What financial information does the current ratio measure? How does the current ratio relate to other liquidity ratios? What are some examples of fixed and variable costs in your workplace?
MA_U10_1-5: analysis, sales % increases, quick ratio, days in inventory, current ratio
MA_U10_1-5: See attached file for problems 1. What type of analysis is indicated by the following? Increase (Decrease*) 2007 2006 Amount Percent Current assets $ 380,000 $ 500,000 $120,000* 24%* Fixed assets 1,680,000 1,500,000 180,000 12% vertical analysis horizontal analysis
Comparisons of acid-test ratio and current ratio
Question is to identify the similarities/differences between acid test ratio and the current ration. Compare/describe how the two ratios meet its current obligation based on similarities/differences/and descriptions.
Financial ratio analysis.
If I have sales, COGS, current assets and liabilities, finished goods, raw materials Work in process, LIFO and % of inventories. How do I calculate gross margin percentage, current ratio and inventory turnover?
Inventory Amount
ABC Company has a current ratio of 3.5 to 1 and an acid-test ratio of 2.8 to 1. Current assets equal $175,000 of which $5,000 consists of prepaid expenses. ABC Company's inventory must be: A) $30,000. B) $40,000. C) $50,000. D) $35,000.
Current Ratio Firms for Violating Agreements
ABC Corporation's current ratio is currently 1.75 to 1. The firm's current ratio cannot fall below 1.5 to 1 without violating agreements with its bondholders. If current liabilities are presently $250 million, the maximum new short-term debt that can be issued to finance an equivalent amount of inventory expansion is: A) $ 41
Current Ratio vs. Total Assets Turnover Ratio
Over the past year, K corporation has realized an increase in its current ratio and a drop in its total assets turnover ratio. However, the company's sales, quick ratio, and fixed assets turnover ratio have remained constant. What explains these changes? Could you share some of your ideas and opinions with us?
Calculating current ratio
Please show calculations Snowball & Company has the following balance sheet: Current assets $ 7,000 A/P & Accruals $ 1,500 Fixed assets 3,000 S-T (3-month) Loans 2,000 Common Stock 1,500
Revenue Recording and Current Ratio
A company has borrowed $3,000,000 to expand its production plant. As a condition for the loan, the bank has required that the company maintain a Current Ratio (current assets divided by total current liabilities) of at least 1.50. On December 15th, the company comptroller reports that the costs of expansion have brought the curr
Company loans: ethics, recording revenue, accounting principle, course of action
A company has borrowed $3,000,000 to expand its production plant. As a condition for the loan, the bank has required that the company maintain a Current Ratio (current assets divided by total current liabilities) of at least 1.50. On December 15th, the company comptroller reports that the costs of expansion have brought the curr
Current ratio and Quick ratio...
In Chater 29, Brealey explains how to use financial ratios to measure the financial performance of a company. He also discusses the effect of financial transactions on financial ratios. This is the question I need answered: If a company borrows a large sum of money from a bank, will the current ratio decrease or increase? When
