A forward contract is a contract made today for the future delivery of an asset at a specified price (strike price). Future contracts are like forward contracts, but are traded on organized exchanges. This makes future contracts more liquid and helps match suppliers with buyers. To help with this process, future contracts are standardized with respect to contract size (standard delivery unit sizes, quantity), delivery arrangments and other specifications like contract length and the quality of goods to be delivered. The buyer will also take delivery of assets through a clearing house, but the seller can usually choose to deliver the asset on any day during the delivery month.
Futures Margins
Because of the risk of default, most exchanges set a "futures margin requirement." That is, for an investor to open and maintain a futures position, they must post a bond worth some portion of the value of the futures contract. This will be posted to a margin account held by the investor's broker.
Initial Margin: The initial amount posted to the margin account equal to some proportion of the value of the futures contract.
Maintenance Margin: If the price of the underlying commodity changes, any losses or gains incurred are added to the margin account. The value of the margin account must stay above the maintanence margin, an amount typically less than the initial margin, to avoid a margin call.
Margin Call: A call from your broke that indicates that the value of your margin account has fallen below the maintenance margin. To continue your future position, you have to top-up your margin account to the initial margin again.
Marked-To-Market: Future contracts are settled daily to minimize default list. That is, gains or losses related to changes in underlying asset prices are posted to margin accounts on a daily bases.
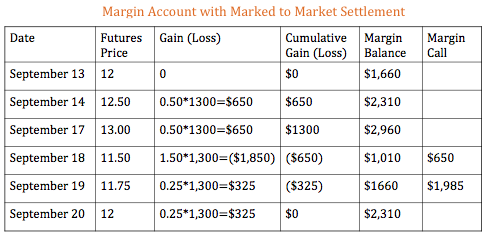
In our previous example (see Derivatives) we discuss how a pineapple farmer and the company Dole might enter into a future contract together for the delivery of 1300 cases of pineapple at $12/case, one year from now. This contract would be worth $15,600. Dole wants to enter into this future contract. The Agricultural Futures Exchange of Thailand requires an initial margin on every contract of $1,660 and a maintenance margin of $1,280. When you opened your futures position, you would make sure you had $1,660 in your account. If the market price of pineapple dropped to $11.50, the loss of $650 ($0.50/case x 1,300 cases) would be posted to Dole's margin account. Because $1,010 ($1660 - $650) is below the required maintenance margin of $1,280, a "margin call" would happen, and Dole's broker would ask the company to bring the account back up to the initial margin amount in order to maintain their futures position.
Hedging with Futures
In our previous example, we discuss how a pineapple farmer and the company Dole might enter into a forward contract together. Because these two parties ("hedgers") have offsetting risks, they can eliminate the risk they each face regarding the future market price of pineapple. They can do the same with a future contract. The farmer and Dole could also transfer their risk to speculators.
Short Futures Hedge: A short futures hedge involves selling a futures contract. Our pineapple farmer might short a futures contract with the intention of minimizing the risk of a drop in price.
Long Futures Hedge: A long futures hedge involves buying a futures contract. Dole might long a futures hedge to minimize the risk of a rise in price.
Photo by Ganapathy Kumar on Unsplash
© BrainMass Inc. brainmass.com April 19, 2024, 2:53 pm ad1c9bdddf